CAS No: 68-26-8
Chemical Name:
(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraen-1-ol
Molecular Formula: C20H30O
Molecular Weight: 286.46
Chemical Structure:
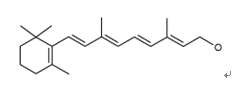
Vitamin A is a fat-soluble
vitamin that is derived from two sources: preformed
retinoids and provitamin A carotenoids.
Preformed retinoids, such as retinol, retinal and retinoic
acid, are found in foods of animal origin like fish,
meat, eggs and full fat milk.
Provitamin A carotenoids like beta-carotene and other
carotenoids (hundreds of different carotenoids are synthesized
by plants, but only about 10% of them are provitamin
A carotenoids) are found in food of plants origin such
as carrots, broccoli leaves, sweet potatoes, kale, spinach,
leafy vegetables, etc.
Beta-carotene and certain carotenoids can be converted
by the body into retinol.
Retinol, the alcohol form, is unstable, vitamin A is
usually produced and administered in a form of retinyl
acetate or palmitate.
Vitamin A deficiency can lead to xerophthalmia (dry
eye) and ultimately to night blindness or total blindness,
as well as to skin disorders, infections (such as measles),
diarrhea, and respiratory disorders.
Retinyl Acetate
CAS No: 127-47-9
Molecular Formula: C22H32O2
Molecular Weight: 328.49
Chemical Structure:

light sensitive, air sensitive: keep tightly closed
in light-resistant containers.
Retinyl Palmitate
CAS No: 79-81-2
Molecular Formula: C36H60O2
Molecular Weight: 524.87
Chemical Structure:
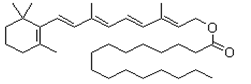
Retinyl palmitate and retinyl acetate are common synthetic
vitamin supplements, they are the ester of retinol (vitamin
A) and palmitic acid, or acetic acid. Both oily form
and dry form are available.
|
