CAS No: 50-81-7
Chemical Name: L-ascorbic acid
Molecular Formula: C6H8O6
Molecular Weight: 176.12
Chemical Structure:
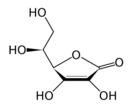
Vitamin C (also called ascorbic
acid), a water-soluble vitamin, is a carbohydrate-like
substance involved in the metabolic functions including
synthesis of collagen (an important protein used to
make skin, scar tissue, tendons, ligaments, and blood
vessels), maintenance of the structural strength of
the blood vessels, metabolism of certain amino acids,
and the synthesis or release of hormones in the adrenal
glands. In the immune system, vitamin C helps the white
blood cells to fight infection, it is essential for
the healing of wounds. It helps the body to absorb iron.
Iron is needed to make haemoglobin, the red pigment
in the blood which transports oxygen from the lungs
to the rest of the body. As an antioxidant, vitamin
C plays an important role in protecting the body from
the harmful effects of too many free radicals which
may harm healthy cells.
Vitamin C deficiency can lead to dry and splitting hair;
gingivitis and bleeding gums; rough, dry, scaly skin;
poot wound-healing, easy bruising; nosebleeds; weakened
enamel of the teeth; swollen and painful joints; anemia;
weak immune function to infections; A severe form of
vitamin C deficiency is known as scurvy, which mainly
affects older, malnourished adults.
The body does not manufacture vitamin C on its own,
nor does it store it. It is therefore important to include
plenty of vitamin C-containing foods in one's daily
diet (primarily fresh fruits and vegetables).
Vitamin C is highly sensitive to light, air and heat.
Consumption of vitamin C-rich foods in their fresh,
raw form is the best way to maximize vitamin C intake.
Standards: BP2004/EP5/USP29
Packing: 25kgs/ctn
Storage: Keep container tightly closed.
Keep container away from light, heat in a cool, well-ventilated
area.
|
