CAS No: 22839-47-0
Chemical Name: N-(L-alfa-aspartyl)-L-phenylalanine,
1-methyl ester
Molecular Formula: C14H18N2O5
Molecular Weight: 294.31
Chemical Structure:
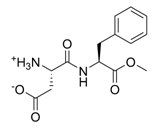
Aspartame is an artificial,
non-saccharide sweetener, a methyl ester of the dipeptide
of the amino acids L-aspartic acid and L-phenylalanine.
It has no negative effect on blood sugar, coronary heart
diseases and hypertension, and it doesn¡¯t cause dental
caries.
Aspartame is commonly used in soft drinks, It is also
used in chewable vitamin supplements and common in many
sugar-free chewing gums. Aspartame is also one of the
sugar substitutes used by people with diabetes.
However, aspartame is not suitable for baking because
it often hydrolyzes (breaks down) into its constituent
amino acids when heated and loses much of its sweetness.
The stability of aspartame under heating can be improved
to some extent by encasing it in fats or in maltodextrin.
The stability when dissolved in water depends markedly
on pH. At room temperature, it is most stable at pH
4.3, where its half-life is nearly 300 days. At pH 7,
however, its half-life is only a few days. Most soft-drinks
have a pH between 3 and 5, where aspartame is reasonably
stable. In products that may require a longer shelf
life, such as syrups, aspartame is sometimes blended
with a more stable sweetener, such as saccharin.
Blends of aspartame with acesulfame potassium are alleged
to taste more like sugar, and to be sweeter than either
substitute used alone.
Standards: FCC IV
Packing: 25kg / ctn, drum
Storage: Keep in a tightly closed container, stored
in a cool, dry, ventilated area. |
