CAS No: 1406-18-4
59-02-9 d-alpha tocopherol (natural)
58-95-7 d-alpha tocopheryl acetate
10191-41-0 dl-alpha tocopherol (artificial)
7695-91-2 dl-alpha tocopheryl acetate
Chemical Name:
(2R)-3,4-Dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-[(4R,8R)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]-2H-1-benzopyran-6-ol
Molecular formula: C29H50O2
Molecular weight: 430.69
Chemical Structure:
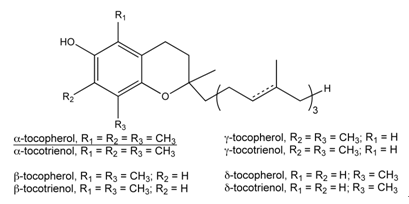
Vitamin E is fat-soluble vitamins
with antioxidant properties. It exists in eight different
forms, four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. Both
the tocopherols and tocotrienols occur in alpha-, beta-,
gamma- and delta- forms. Each form has slightly different
biological activity, alpha-tocopherol is the most active
form of vitamin E that is preferentially absorbed and
accumulated in humans. The synthetic form is labeled
"DL-" while the natural form is labeled "D-".
The synthetic form is not as active as the natural form.
Vitamin E protects body tissue from damage caused by
unstable substances called free radicals, which can
harm cells, tissues, and organs.
Vitamin E is also important in the formation of red
blood cells and helps the body to use vitamin K.
Vegetable oils, nuts, green leafy vegetables are common
food sources of vitamin E. Most natural vitamin E is
derived from vegetable oils, usually soybean oil.
Generally commercial vitamin E supplement is synthetic
vitamin E, the most common form is acetate ester.
|
