CAS No: 50-21-5
L: 79-33-4
D: 10326-41-7
D/L: 598-82-3
Chemical Name: 2-hydroxypropanoic acid
Molecular Formula: C3H6O3
Molecular Weight: 90.08
Chemical Structural:
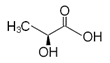
Lactic acid is a carboxylic
acid. It is chiral and has two optical isomers. One
is known as L-(+)-lactic acid or (S)-lactic acid and
the other, its mirror image, is D-(-)-lactic acid or
(R)-lactic acid. L-(+)-Lactic acid is the biologically
important isomer.
Most commercially used lactic acid is derived by using
bacteria such as Bacillus acidilacti, Lactobacillus
delbueckii or Lactobacillus bulgaricus to ferment carbohydrates
from nondairy sources such as cornstarch, potatoes and
molasses.
Lactic acid is usually used as a pH adjusting ingredient,
or as a preservative (either as antioxidant or for control
of pathogenic micro-organisms) in various processed
foods. It may also be used as a fermentation booster
in rye and sourdough breads.
Lactic acid is widely used for inhibiting pathogenic
bacteria like E.coli, Salmonella, Campylobacter and
Listeria on animal carcasses like beef, pork and poultry
during the slaughtering process.
Potassium lactate, sodium lactate and calcium lactate
are the neutralized salts of lactic acid. Potassium
lactate is used in many fresh and cooked meat products
for shelf life control, color preservation and reduction
of sodium content. Sodium lactate has a mild saline
taste and is therefore suitable for flavour enhancement
in meat products as well. Sodium lactate is being produced
as liquids as well as powders. Calcium lactate is popular
for fortification and improved texture in emulsified
meat products like frankfurters.
Standards: FCC IV
Packing: 25kg / PE drum
Storage: Keep container tightly closed. Keep in a cool,
dry, well-ventilated place.
|
